Continuing from our last data snapshot, we take a closer look at companies categorized as “Startup” in CSET’s Private-sector AI-Related Activity Tracker (PARAT). A company receives the “Startup” designation when its last funding rounds are raised in early-stage rounds (e.g., seed or angel). There are 55 companies categorized as “Startup” in PARAT.
To look at “Startup” companies with AI-related outputs, we filter for companies with at least one AI publication or AI patent. Publications are assigned to companies by using author affiliation data, and determined to be AI-relevant using an AI publication classifier. Patents are assigned to companies by the current assignee or the original assignee, and determined to be AI-relevant using Cooperative Patent Classifications.
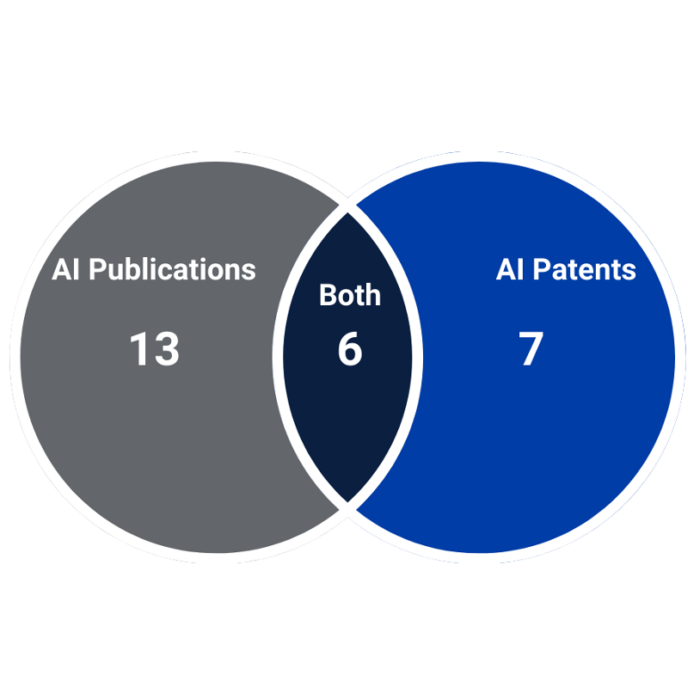
This AI publication and AI patent filter results in 26 “Startup” companies: 19 companies with AI publications (35 percent of all “Startup” companies), 13 companies with AI patents (24 percent of all “Startup” companies), and six companies with both AI publications and patents (11 percent of all “Startup” companies). Figure 1 displays the number of companies by type of AI output.
Figure 1. PARAT “Startup” Companies by Type of AI Output
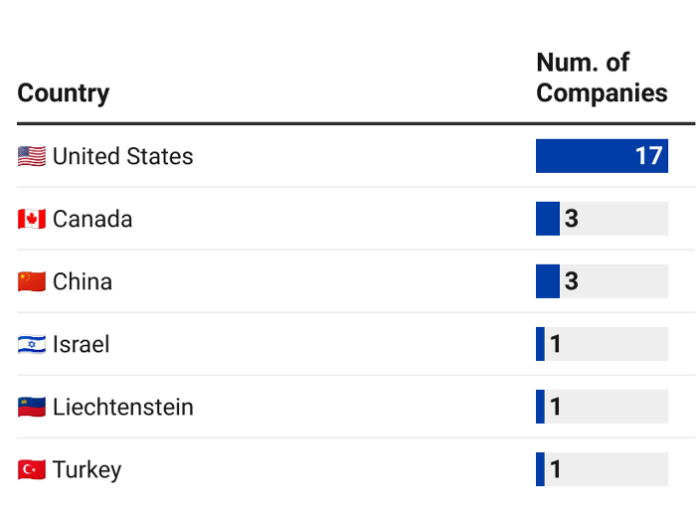
In Figure 2, we display the 26 companies with AI publications and/or AI patents according to their headquarters location. Most of the “Startup” companies in PARAT with AI output are based in the United States.
Figure 2. Breakdown of PARAT “Startup” Companies with AI Output by Country
Looking at the description of these “Startup” companies in Crunchbase and on their websites, we see that they encompass a wide range of AI applications. Below are some ways these companies report using AI technologies:
- Computer vision technologies for airport scanners (Synapse Technology);
- Machine learning technologies for optimizing manufacturing pipelines (DarwinAI);
- A smart home system to improve senior living (Caspar.AI);
- An app for crypto exchange and financial technology support (Nash);
- Scientific and engineering support to defense and industry (Torch Technologies);
- Human-computer interaction for adaptive learning (Enlearn); and
- Autonomous driving and intelligent transportation services (AIsimba).
Next, we provide more details on three “Startup” companies in PARAT that have at least one AI publication or AI patent.
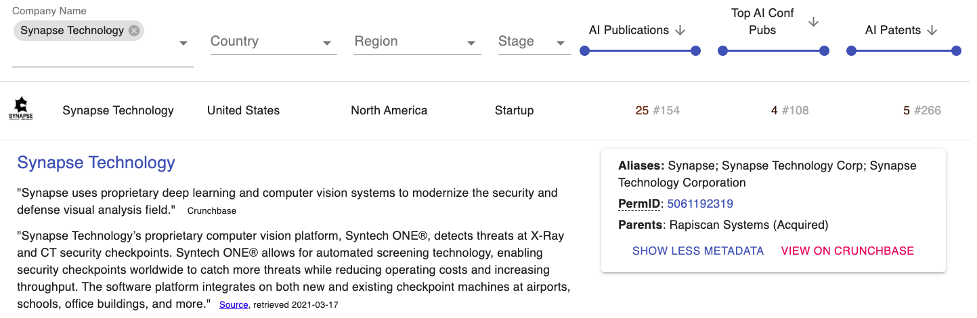
Synapse Technology Corporation, a U.S.-based company, focuses on computer vision technology. They have multiple AI patents, such as “Generating Graphical Representations of Scanned Objects” and “Computer System and Method for Improving Security Screening.”
Figure 3. Synapse Technology PARAT Profile
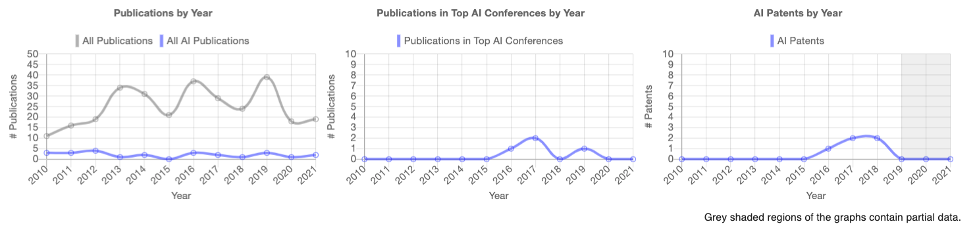
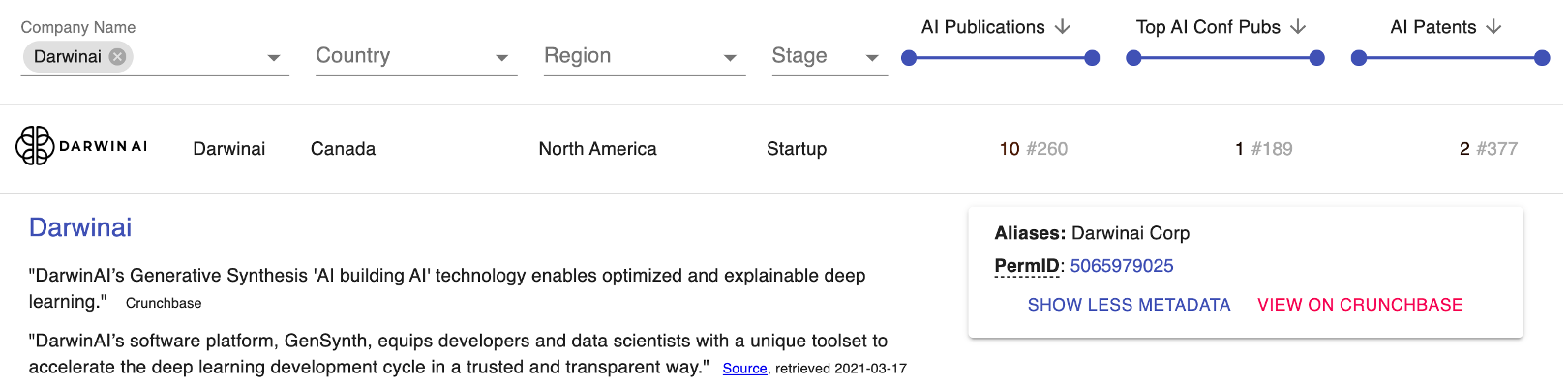
Darwin AI, a canadian-based company, provides a software platform that assists companies in implementing deep learning in a trusted and transparent manner. Their research focuses on image detection. For example their research publications include “CancerNet-SCa: Tailored Deep Neural Network Designs for Detection of Skin Cancer from Dermoscopy Images” and “Towards computer‑aided severity assessment via deep neural networks for geographic and opacity extent scoring of SARS-CoV-2 chest X-rays.” Additionally, Darwin AI has some AI patents, such as “System and Method for Automatic Building of Learning Machines Using Learning Machines.”
Figure 4. Darwin AI PARAT Profile
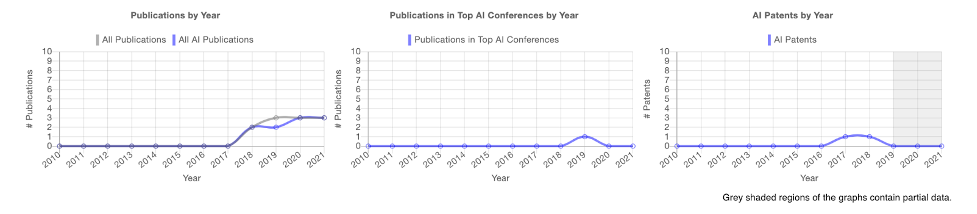
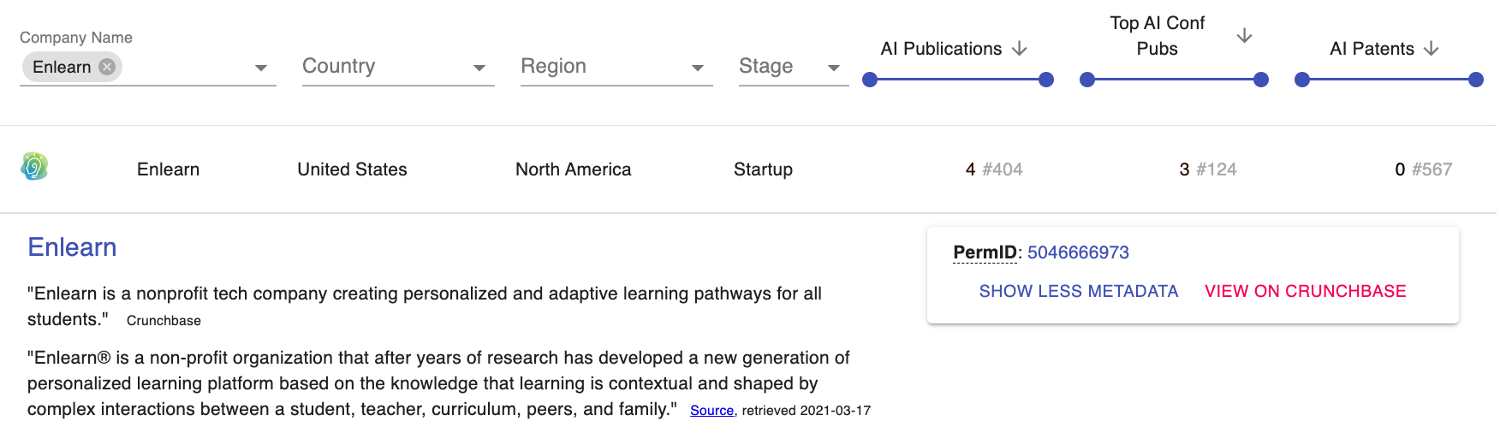
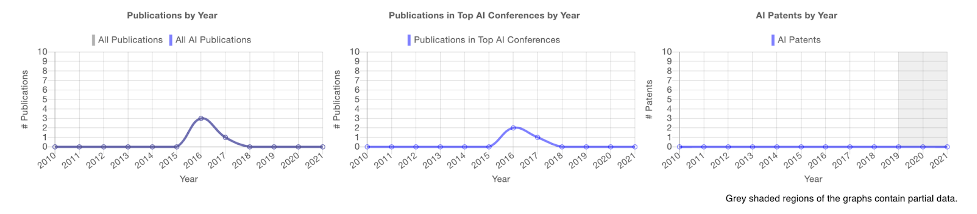
Enlearn is a non-profit organization founded by academics that focuses on advancing scientific learning and education technology. Examples of their publications at the AAAI Conference in Artificial Intelligence (in our top AI conference list) include “Offline Evaluation of Online Reinforcement Learning Algorithms” from 2016, and “Where to Add Actions in Human-in-the-Loop Reinforcement Learning” from 2017.
Figure 5. Enlearn PARAT Profile
Our next data snapshot will highlight companies categorized as “Growth” in PARAT.