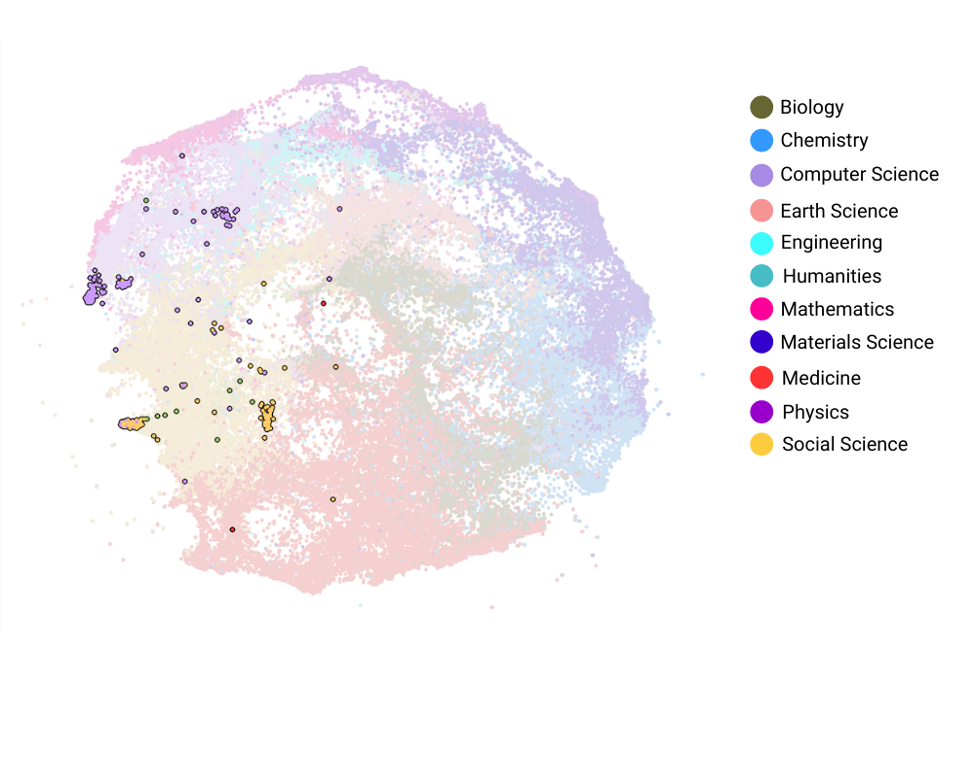
In this snapshot, we analyze natural language processing paper concentrations across research clusters in our Map of Science using the labelling convention described in Defining Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, and Robotics Research Clusters.1 We examine the 397 RCs (as of July 29, 2021) with concentrations of AI papers of at least 25 percent and concentrations of NLP papers of at least 25 percent with the concentration of NLP papers higher than concentration of computer vision- or robotics-related papers. These RCs are referred to here as NLP RCs. Figure 1 displays these RCs within the Map of Science, with RCs color coded by their broad research area.
NLP employs text data across a myriad of domains, including social media analysis, education, surveillance, and more, with methods such as sentiment analysis (i.e., using machine learning to intelligently detect the emotions behind text, such as deciphering between positive and negative product and service reviews) and topic modelling (i.e., using machine learning to break up text data, such as abstracts or articles, into subgroups). An example of widespread application of NLP are “bots” on social media sites such as Twitter. These bots potentially contribute to the spread of misinformation, as well as harassment and online trolling.2
Figure 1. NLP RCs Highlighted in the Map of Science
Table 1. Number of Natural Language Processing RCs by Broad Research Area
| Broad Research Area | Number of RCs | Percentage of NLP RCs |
| Computer Science | 352 | 89% |
| Social Science | 39 | 10% |
| Humanities | 3 | < 1% |
| Mathematics | 2 | < 1% |
| Medicine | 1 | < 1% |
We found that the overwhelming majority of NLP RCs fall within computer science, as shown in Table 1. The remaining RCs are largely social science RCs plus a few Humanities, Mathematics, and Medicine NLP RCs. Table 2 illustrates the concentration of NLP papers across all NLP RCs. We found that about one-fourth of NLP RCs actually have a concentration of over 75 percent NLP-related papers, suggesting that these NLP RCs are NLP-focused rather than employing NLP as an accessory field of research.
Table 2. NLP Concentrations Across RCs
| Percentage of NLP-Related Publications | Number of RCs |
| (10%, 25%] | 5 |
| (25%, 50%] | 150 |
| (50%, 75%] | 144 |
| (75%, 100%] | 98 |
| Total | 397 |
In order to understand the range of RCs that can be assigned the NLP label, we provide details on four RCs:
- The NLP RC with the highest percentage of NLP-related publications
- The NLP RC with the lowest percentage of NLP-related publications
- A NLP RC in non-computer science (CS) STEM field
- A NLP RC in a non-STEM field
For each of these RCs, we provide the top five core papers. Core papers are publications that have strong citation links within an RC, meaning that they have high citations from the other publications in that cluster. Since RCs do not necessarily represent a homogenous area of research, we can review the member publications to describe the central areas of research that a RC is focused on.
NLP RC with the highest percentage of NLP papers
Of RC 60531’s 727 papers, 95 percent are NLP related. RC 60531 focuses broadly on machine translations, word embeddings, speech recognition, and NLP methods. Like most NLP RCs, it falls under the computer science research realm. Additionally, this RC is forecasted to experience extreme growth, meaning a forecasted mean growth of 8 percent or more over the next three years.3
RC 60531 Top Five Core Papers:
- A robust self-learning method for fully unsupervised cross-lingual mappings of word embeddings
- How to (Properly) Evaluate Cross-Lingual Word Embeddings: On Strong Baselines, Comparative Analyses, and Some Misconceptions
- Learning bilingual word embeddings with (almost) no bilingual data
- Word Translation Without Parallel Data
- Offline bilingual word vectors, orthogonal transformations and the inverted softmax
Three-fourths of papers had country affiliations; two-fifths of papers with data available on country affiliations were affiliated with the United States, while less than one-fourth of them were affiliated with China.
NLP RC with the lowest percentage of NLP papers
RC 47196 falls into the computer science area of research, like most NLP RCs. Just over 25 percent of its 670 papers are NLP-related. This RC broadly focuses on data mining, knowledge extraction, and related linguistics analytic methods. Less than one-third of its papers also are AI-related.
RC 47196 Top Five Core Papers:
- 短视频对城市旅游景点的呈现与传播——以“抖音”为例
- Research on the Classification of Travel Demand Information and the Acquisition of Ontology Concept Based on “We Media”, 2015, 图书情报工作
- Automatic Extraction of Nonlinguistic Representations of Texts to Support Writing
- Text Classification for Student Data Set using Naive Bayes Classifier and KNN Classifier
- Development of Game Application for Enhancement of Children’s Cognitive Skills
This RC is led by India and had fewer new papers published last year than the year prior (i.e., had negative growth).
Examining a non-CS STEM NLP RC
While most NLP RCs are in the CS research domain, it is useful to assess the makeup of non-CS related RCs. Cluster 26223 focuses on mathematics and more than 70 percent of its papers are NLP-related. This cluster is 14 years old and contains 1,507 papers, dominated by the United States.
While this RC focuses primarily on mathematics, computer science, linguistics, and NLP, its closest neighbors also focus on epistemology, literature, AI, and various humanities fields. RC 26223 grew about 4 percent last year, and extreme growth is not forecasted for this RC.
RC 26221 Top Five Core Papers:
- The Grammar of Degree: Gradability Across Languages
- Modification (book)
- The semantics of many, much, few, and little
- Projecting adjectives in Chinese
- Semantic variation and the grammar of property concepts, 2015, Language
A non-STEM NLP RC
Social science is a distant second place to CS for general fields of study for RCs. RC 3916 is an example of a social science-focused RC with a high concentration of NLP papers: more than 50 percent of its 4749 papers are NLP papers.
RC 3916 contains psychology, communication, and syntax papers with an evident focus on the study of sign language. This RC grew 47 percent last year and is led by the United States.
RC 3916 Top Five Core Papers:
- Gesture, sign, and language: The coming of age of sign language and gesture studies
- Interaction of Morphology and Syntax in American Sign Language
- Modification of indicating verbs in British Sign Language: A corpus-based study
- The syntax of sign language agreement: Common ingredients, but unusual recipe
- Visible Meaning: Sign language and the foundations of semantics
If you missed it, find the first part of the series exploring computer vision-related RCs, and other snapshots examining the Map of Science, below.
In August 2021, CSET updated the Map of Science, linking more data to the research clusters and implementing a more stable clustering method. With this update, research clusters were assigned new IDs, so the cluster IDs reported in this Snapshot will not match IDs in the current Map of Science user interface. If you are interested in knowing which clusters in the updated Map are most similar to those reported here, or have general questions about our methodology or want to discuss this research, you can email cset@georgetown.edu.
Download Related Data Brief
Comparing China’s and the United States’ Leading Roles in the Landscape of Science- https://cset.georgetown.edu/publication/defining-computer-vision-natural-language-processing-and-robotics-research-clusters/
- E.g.: https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2018/04/09/bots-in-the-twittersphere/; https://arxiv.org/pdf/2012.02164.pdf; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8139392/
- See AI Bin RC average growth vs. forecast growth paper by Autumn Toney: https://cset.georgetown.edu/publication/measuring-ai-rc-growth/