The GitHub snapshot series primarily focuses on how repository- and owner-specific metadata sheds light on broader questions regarding software development and proliferation. However, the individual stories of major repositories and owners get lost when tackling such broad questions. To highlight the various aspects and benefits of GitHub discussed throughout the series, this snapshot will focus on one of the most popular machine learning repository owners on the platform: HuggingFace.
If you have ever experimented with or implemented machine learning into one of your projects, there is a good chance you utilized HuggingFace’s work—either knowingly or unknowingly. Originally a chatbot company, HuggingFace now partners with more than 5,000 organizations, including Intel, the Allen Institute for AI, and Google AI, to develop state of the art AI systems. Their open source packages aim to tackle a variety of tasks, including but not limited to: image classification, object detection, text generation, conversational models, reinforcement learning, speech recognition, and text-to-image processing. Today, HuggingFace offers users more than 80,000 models and more than 12,000 datasets across these different tasks. Each model type and dataset comes with a set of installation and use instructions, streamlining the process of training to application for even brand-new users. Similar to Microsoft, HuggingFace also offers a premium paid service to AI developers who wish to rapidly scale and advance their systems.
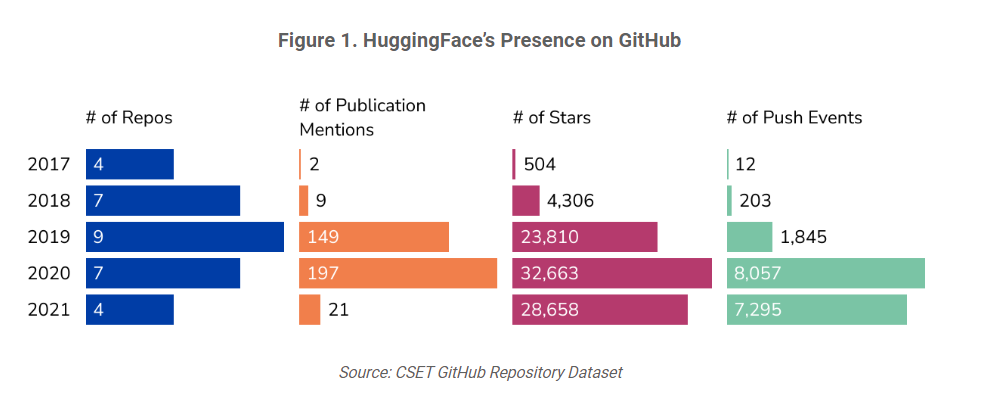
Figure 1. HuggingFace’s Presence on GitHub
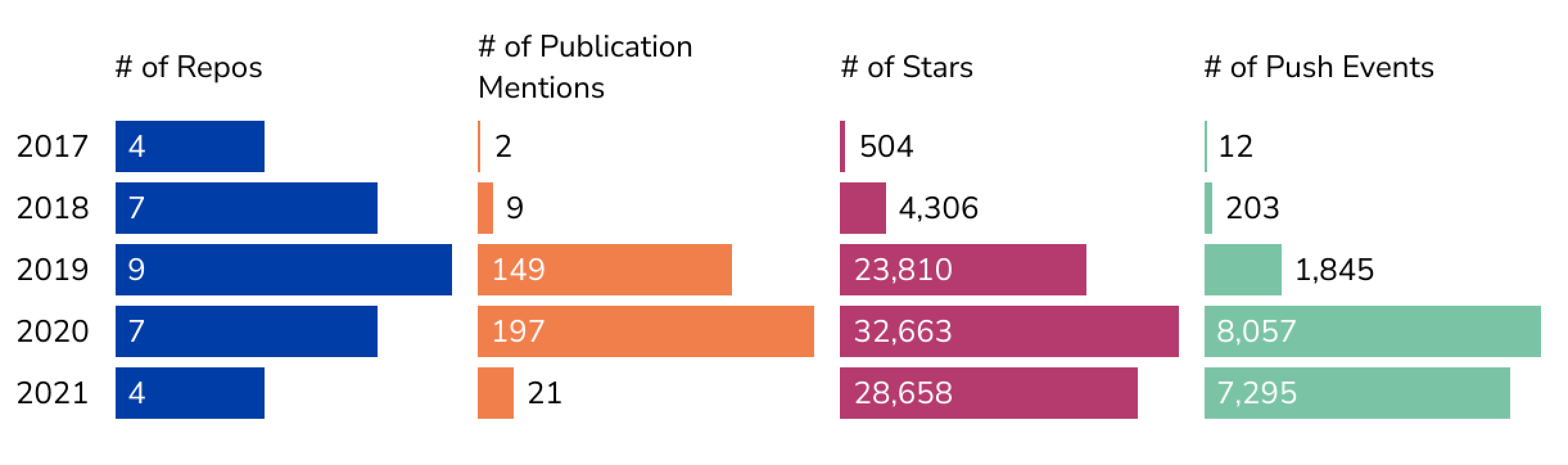
Figure 1 shows HuggingFace’s journey on GitHub through 2021. It shows how many repositories HuggingFace has made public per year since 2017. To find the number of publication mentions, each repository was linked to CSET’s merged corpus of scholarly literature, including Digital Science Dimensions, Clarivate’s Web of Science, Microsoft Academic Graph, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, arXiv, and Papers With Code.1 The numbers of stars and push events were collected from each repository’s specific metadata and aggregated by year. The rapid rise in 2019 stemmed from a flurry of activity by HuggingFace. By the start of the year, its Natural Language Processing models were already in use by more than 1,000 companies. In the AI/ML space, HuggingFace released its cache of NLP models Transformers to the TensorFlow machine learning framework, further expanding the use cases of its open source models. In the financial space, HuggingFace continued to attract funding, including $15 million from a group of capital investors.
The journey from chatbot company to global leader in AI/ML systems may seem relatively straightforward—chatbots rely upon the very systems HuggingFace crafts for both public and private use cases. HuggingFace’s ability to attract both corporate partners and serious venture capital funding, along with its own inherent need for state-of-the-art NLP models, certainly set it upon the path to success. However, many other software companies with partnerships and funding fail to grow as rapidly as HuggingFace. HuggingFace achieved its colossal status by recognizing the value in and dedicating itself to open source software. Any major project, whether in academia or industry, that utilized HuggingFace’s library of publicly available models spread the company’s name. The overall efficiency and update frequency made HuggingFace a natural fit for most organizations’ development cycles. Fully developed and implemented machine learning solutions often require significant investments from the company. HuggingFace continues to provide alternatives to the developmental costs associated with machine learning and AI and to democratize emerging technology by hosting state-of-the-art solutions, as evidenced by its recently announced Inference Endpoints service. Open source software, hosted on sites like GitHub, provides a mechanism for improvement with fewer barriers to entry.
- CSET’s merged corpus of scholarly literature includes Digital Science’s Dimensions, Clarivate’s Web of Science, Microsoft Academic Graph, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, arXiv, and Papers With Code. Data sourced from Dimensions, an inter-linked research information system provided by Digital Science (http://www.dimensions.ai). All China National Knowledge Infrastructure content is furnished for use in the United States by East View Information Services, Minneapolis, MN, USA.