We have previously examined “Startup” and “Growth” companies listed in CSET’s Private-sector AI-Related Activity Tracker (PARAT). Here, we provide details on “Mature” companies listed in PARAT. The “Mature” designation is the final stage of company development in PARAT. A company is considered “Mature” when it meets one or more of the following criteria: it is publicly traded, has more than 1,000 employees, or raised funding in late-stage venture capital or private equity rounds (e.g., Series D or post-IPO rounds). There are 698 companies categorized as “Mature” in PARAT.
When filtering for “Mature” companies that have at least one AI publication or AI patent, we find 484 such companies: 124 with AI publications (18 percent of all “Mature” companies), 67 with AI patents (10 percent of all “Mature” companies), and 293 with both AI publications and patents (42 percent of all “Mature” companies). Figure 1 displays the breakdown of the number of companies by type of AI output.
Figure 1. PARAT “Mature” Companies by Type of AI Output
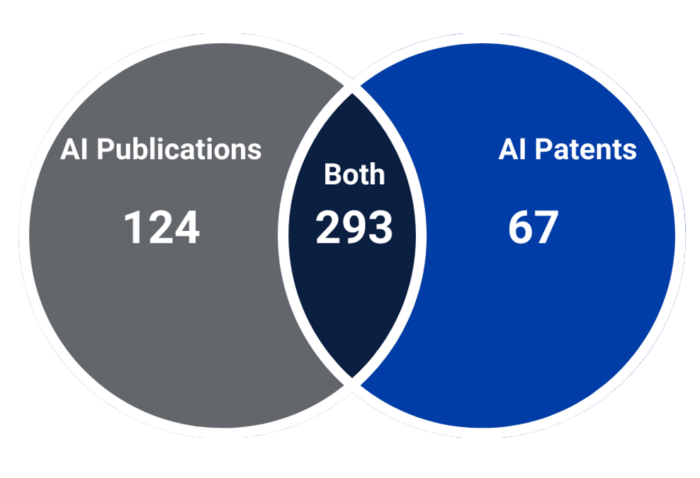
When we compared “Growth” to “Startup” companies, we saw that 36 percent of “Growth” companies produced AI publications and AI patents (compared to a mere 11 percent of “Startup” companies). We see this trend continuing, with 42 percent of “Mature” companies producing both.
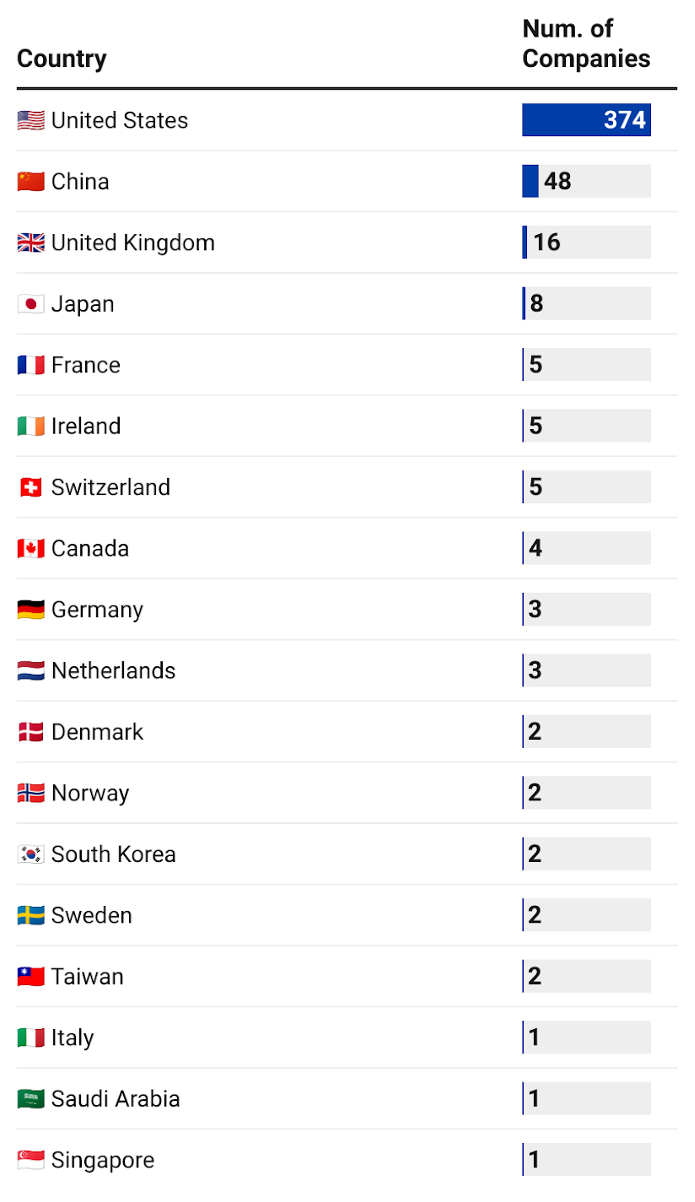
In Figure 2, we present the 484 “Mature” companies with AI publications or AI patents by their headquarters location. Recall that PARAT data does not contain all global companies engaged in AI activity and likely overrepresents U.S.-based companies. As with “Startup” and “Growth” companies, most of the “Mature” companies in PARAT are based in the United States.
Figure 2. Breakdown of PARAT “Mature” Companies with with AI Output by Country
“Mature” companies in PARAT include many companies typically associated with cutting-edge AI research and technology, such as Google, Microsoft, Facebook, IBM, and Amazon. Because these companies have extensive resources and are leading AI development, they have a wide range of AI outputs and applications. For example, Amazon is more than just an e-commerce company, it also provides cloud-computing and digital streaming services.
As a result of their resources and focus on AI research, many of the “Mature” companies in PARAT publish frequent and notable work, with dedicated research departments that focus on various subfields of AI and machine learning. To highlight “Mature” companies’ AI research and AI patent output, we provide some examples of their recent work.
For AI research publications we looked at one of the top AI and machine learning conferences: Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). At the NeurIPS 2021 conference, six papers were given Outstanding Paper awards, and four of those six papers had at least one “Mature” company-affiliated author:1
- A Universal Law of Robustness via Isoperimetry (Microsoft);
- On the Expressivity of Markov Reward (DeepMind, which is a subsidiary of Google’s parent company Alphabet);
- Deep Reinforcement Learning at the Edge of the Statistical Precipice (Google); and
- Moser Flow: Divergence-based Generative Modeling on Manifolds (Facebook).
For AI patenting activity among “Mature” companies in PARAT, we looked for patents granted to a “Mature” company in the last five years that were highly cited by other patents. Two such patents come from Samsung and IBM, two of the more prolific patenters among “Mature” PARAT companies. With 190 citations, Samsung’s 2016 patent “Techniques for autonomic reverting to behavioral checkpoints” improves the creation and capture of mobile device checkpoints without impeding the device’s performance or increasing its power consumption. With 468 citations, IBM’s 2020 patent “Dynamic montage reconstruction” contains “systems and methods for storing, accessing, and utilizing information regarding medical image montages.”2
This snapshot is the last one highlighting various company stages of development in PARAT. The next snapshot will conclude this series with an overview of what to expect in the forthcoming updated and expanded PARAT tool!
- https://blog.neurips.cc/2021/11/30/announcing-the-neurips-2021-award-recipients/
- Reicher, Murray A. “Dynamic montage reconstruction,” U.S. Patent No. 10,579,903, March 3, 2020.