The following document details China’s plans to develop domestic standards for the smart manufacturing industry.
The Chinese source text is available online at: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-12/09/5659548/files/e0a926f4bc584e1d801f1f24ea0d624e.pdf
An archived version of the Chinese source text is available online at: https://perma.cc/56QG-GKPL
U.S. $1 ≈ 6.4 Chinese Yuan Renminbi (RMB), as of February 17, 2022.
Guidelines for the Construction of a
National Smart Manufacturing Standards System
(2021 edition)
November 2021
Contents
I. Smart Manufacturing System Architecture 1
II. General Requirements 3
(i) Basic Principles 4
(ii) Construction Goals 5
III. Construction Philosophy 5
(i) Structure of the Smart Manufacturing Standards System 5
(ii) Smart Manufacturing Standards System Framework 7
IV. Construction Content 9
(i) Foundational and General Purpose Standards 9
(ii) Key Technical Standards 12
(iii) Industry Application Standards 28
V. Organization and Implementation 32
I. Smart Manufacturing System Architecture
Smart manufacturing is an advanced production method based on the in-depth integration of advanced manufacturing technology and new generation information technology. It extends throughout the entire product life cycle, including design, production, management, and service, and has the characteristics of self-perception, self-decision-making, self-execution, self-adaptation, and self-learning. Smart manufacturing aims to improve the quality, benefits from efficiency, and flexibility of the manufacturing industry.
The smart manufacturing system architecture describes the elements, equipment, and activities involved in smart manufacturing from three dimensions: life cycle, system levels, and intelligent features. It is mainly used to clarify the standardized objects and scope of smart manufacturing. The smart manufacturing system architecture is shown in Figure 1.
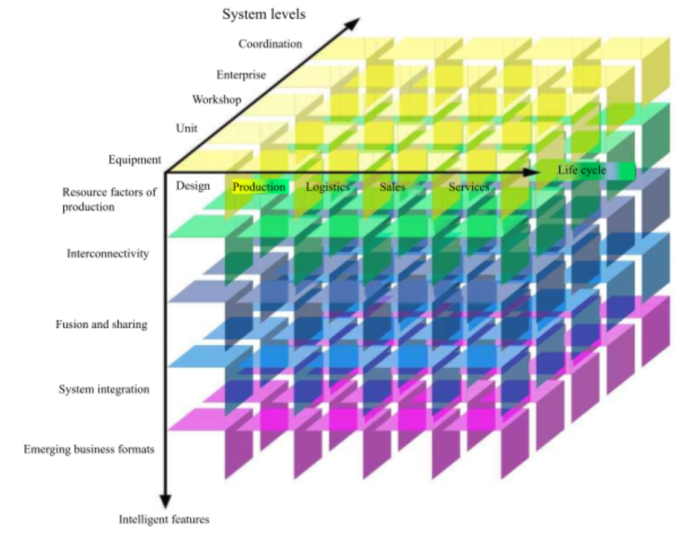
1. Life Cycle
The life cycle covers the various stages from product prototype development to product recycling and remanufacture, including mutually linked value-creation activities such as design, production, logistics, sales, and service. The various activities of the life cycle can be iterated and optimized, featuring characteristics such as sustainable development. The life cycle composition and time sequence will differ between different industries.
- Design is the process of implementing and optimizing requirements based on all enterprise constraints and selected technologies.
- Production is the process of creating a product, including activities such as the processing, transporting, assembling, and testing of materials.
- Logistics is the process by which goods physically flow from the place of supply to the place of receipt.
- Sales refers to the business activities by which products or goods are transferred from enterprises into the hands of customers.
- Service refers to the series of actions produced by the interaction between product provider and customer as well as their results.
2. System levels
For the rest of the translation, download the PDF below.