Our last data snapshot focused on “Startup” companies in CSET’s Private-sector AI-Related Activity Tracker (PARAT). We now highlight the companies categorized as “Growth.” A company in PARAT receives the “Growth” designation when its last funding round was raised in mid-stage rounds (e.g., Series A-C). There are 260 companies categorized as “Growth” in PARAT.
When we filter for “Growth” companies that have at least one AI publication or AI patent, we see 188 such companies in PARAT: 63 with AI publications (24 percent of all “Growth” companies), 30 with AI patents (16 percent of all “Growth” companies), and 95 with both AI publications and patents (36 percent of all “Growth” companies). Below, Figure 1 displays the number of companies by type of AI output.
Figure 1. PARAT “Growth” Companies by Type of AI Output
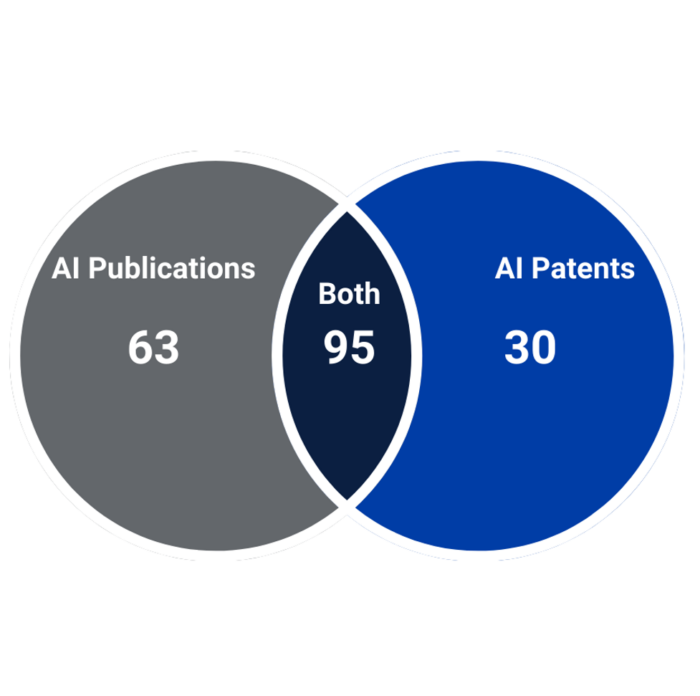
There is a notable, but expected, difference between the number of “Growth” companies with both AI publications and AI patents and the number of “Startup” companies with both. Only 11 percent of “Startup” companies in PARAT have both AI publications and AI patents, whereas 36 percent of “Growth” companies have both.
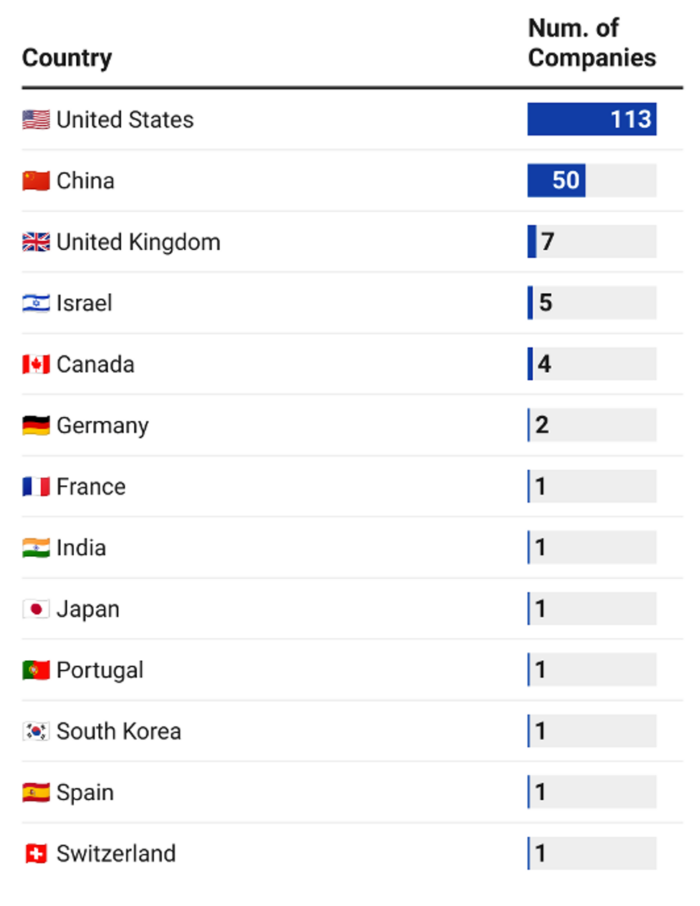
In Figure 2, we display the 188 “Growth” companies with AI publications and/or AI patents according to their headquarters location. It is important to note that the list of companies in PARAT is not necessarily representative of all global companies with some degree of AI activity. Like “Startup” companies, most “Growth” companies in PARAT are based in the United States.
Figure 2. Breakdown of PARAT “Growth” Companies with AI Output by Country
Similar to the “Startup” companies, when we look at these “Growth” companies on Crunchbase and on their websites, we find that they focus on a wide range of AI applications:
- Computer vision for medical imaging (Deepwise);
- AI technology for smart homes, smart surveillance, smartphones, robots, drones, and Internet-of-Things devices (Kneron);
- AI technology and software products for company support (Element AI);
- Humanoid robot manufacturing (UBTECH Robotics);
- Machine learning technologies for sustainable engineering (PROWLER.io);
- Computer vision technology for the retail industry (Malong); and
- AI technologies to connect people, devices, and services (Emotibot).
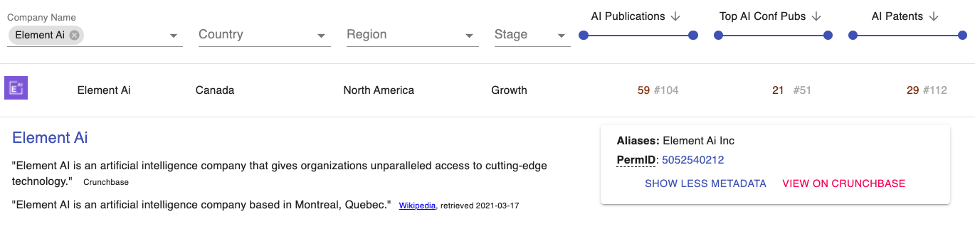
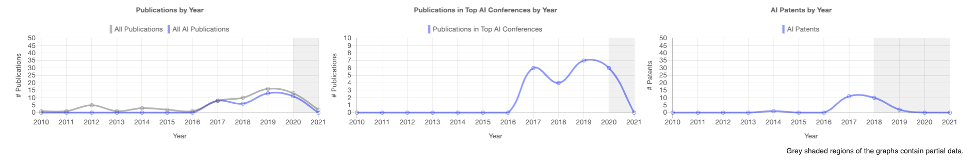
Canada-based Element AI is a company that employs researchers and data scientists to conduct cutting-edge AI research and has many AI publications and patents. In 2020 alone, 10 of its 17 paper submissions to the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) were accepted. Emphasizing AI research, Element AI lists its publications online. The company also has AI patents, such as “Training method for convolutional neural networks for use in artistic style transfers for video” filed in 2018.
Figure 3. Element AI PARAT Profile
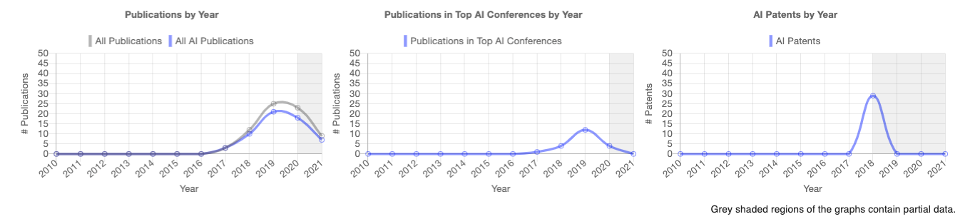
China-based Malong, a company that focuses on computer vision technology, has published at many different top AI conferences, including IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), and European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV)1 One of its papers, “Cross-Batch Memory for Embedding Learning,” was nominated for best conference paper at CVPR 2020.
Figure 4. Malong PARAT Profile

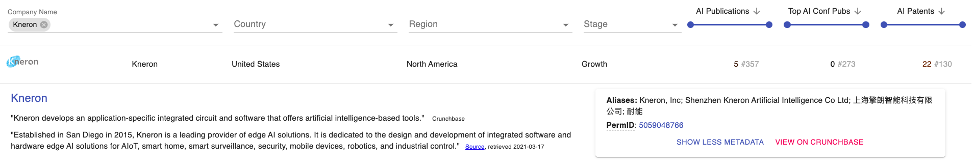
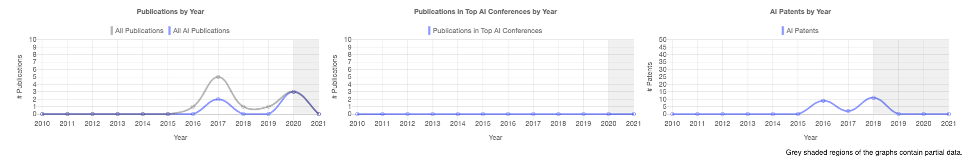
U.S.-based Kneron has mainly AI patent output. The company name comes from combining the words “knowledge” and “neuron,” symbolizing the company’s belief in leading AI technology. Its AI patents include “Pooling operation device and method for convolutional neural network” and “Multi-layer artificial neural network and controlling method thereof.”
Figure 5. Kneron PARAT Profile
In our next data snapshot, we will highlight companies categorized as “Mature” in PARAT.